[ad_1]
Finite Aspect Evaluation (FEA) is a robust numerical method used to research and remedy complicated engineering issues. By dividing a posh construction or system into smaller, extra manageable parts, FEA allows engineers to simulate and predict the habits of varied bodily phenomena. This text gives a complete overview of finite ingredient evaluation, its functions, advantages, limitations, and future traits.
Finite Aspect Evaluation, also referred to as FEA, is a computational technique used to acquire approximate options for varied engineering issues. It entails dividing a posh geometry or system into finite parts, therefore the title, and making use of numerical strategies to research the habits of every ingredient. By combining the behaviors of all the weather, engineers can achieve precious insights into the general efficiency of the system beneath completely different circumstances.
Historical past and Growth of Finite Aspect Evaluation
The event of FEA will be traced again to the early Forties and has since undergone vital developments.
The origins of FEA will be attributed to the work of researchers like Richard Courant, Kurt Friedrichs, and John von Neumann, who developed numerical strategies for fixing partial differential equations throughout World Battle II. These strategies, referred to as the finite distinction technique, shaped the premise for the later growth of FEA.
Within the Nineteen Fifties and Nineteen Sixties, the finite ingredient technique (FEM) started to take form as a extra versatile and correct method to numerical evaluation. Engineers and mathematicians, together with Ray W. Clough, Richard H. Gallagher, and Olgierd C. Zienkiewicz, performed essential roles in creating and popularizing the FEM.
The arrival of digital computer systems within the Nineteen Sixties and Nineteen Seventies allowed for the sensible implementation of FEA. Early FEA packages had been restricted by the computational sources obtainable on the time. Nonetheless, as computer systems grew to become extra highly effective, FEA gained wider acceptance and started for use in trade for fixing real-world engineering issues.
Within the Nineteen Eighties and Nineties, FEA software program grew to become extra refined, providing superior capabilities and user-friendly interfaces. The event of economic software program packages, comparable to ANSYS, MSC Nastran, and Abaqus, made FEA accessible to engineers and expanded its functions throughout varied industries.
Through the years, FEA has advanced to embody a variety of research sorts, together with structural evaluation, thermal evaluation, fluid move evaluation, and electromagnetic evaluation. It has turn out to be a vital software in product design, optimization, and digital prototyping, permitting engineers to foretell and consider the habits of buildings and techniques beneath completely different circumstances with out the necessity for bodily testing.
Developments in computing energy, numerical algorithms, and modeling strategies have additional improved the accuracy and effectivity of FEA. Researchers proceed to refine and improve the tactic, enabling extra complicated and detailed simulations.
Lately, FEA has additionally benefited from integration with different applied sciences comparable to computer-aided design (CAD), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and optimization algorithms. This integration has enabled multidisciplinary evaluation and optimization, resulting in extra environment friendly and modern engineering options.
Understanding the Finite Aspect Methodology
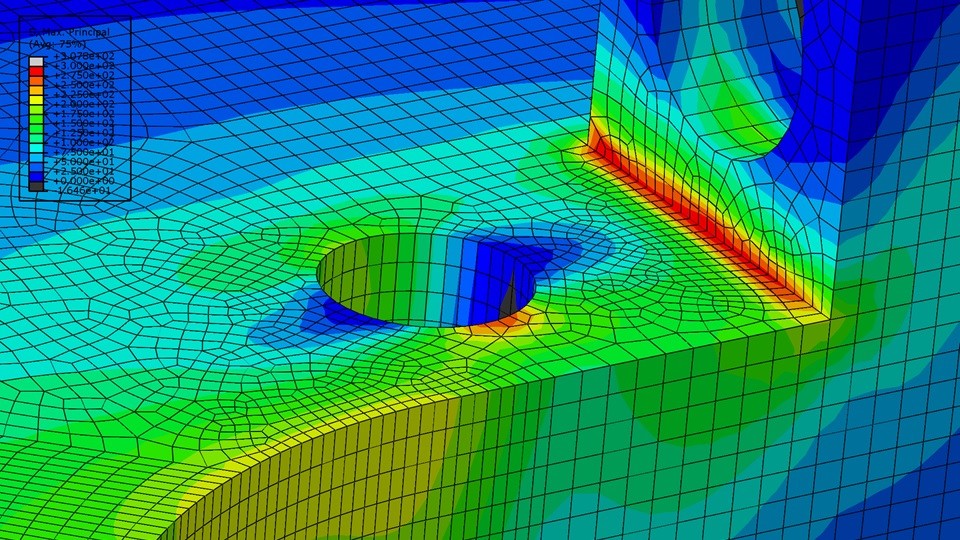
On the core of finite ingredient evaluation lies the Finite Aspect Methodology (FEM). FEM is a numerical method that approximates the habits of a system by dividing it into smaller parts, every represented by a set of mathematical equations. These equations take into account the properties and interactions of the weather, permitting engineers to simulate and predict the habits of your entire system.
The method of finite ingredient evaluation entails a number of steps. First, the geometry of the system is discretized into smaller parts, which will be easy shapes like triangles or quadrilaterals in two dimensions or tetrahedra or hexahedra in three dimensions. Subsequent, the properties and governing equations for every ingredient are outlined. These equations are then solved iteratively to acquire approximate options for your entire system.
[ad_2]




